SIAT Research
-
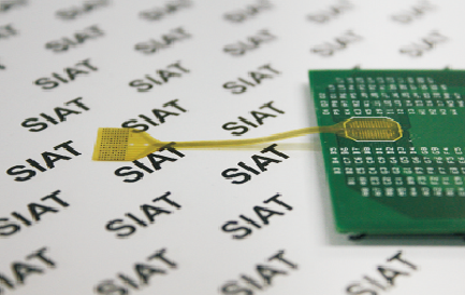
Mar 16, 2020Newly Proposed Strategy Offers Smart Flexible Neural Electrode with High EfficiencyProf. WU Tianzhun’s group at Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, based on their previous work on neural interfaces (Electrochia Acta, Advanced Materials Interf... With the rapid development of smart flexible electronics in wearable and implantable fields, it is urgent to prepare biomimetic electrode materials efficiently with simple operation, good biocompat...
-
Mar 13, 2020Scientists Develop Fluoroxalate Cathode Material for Potassium-Ion Batteries with Ultra-long CyclabilityA research group led by Prof. TANG Yongbing and his team members (JI Bifa, Dr. YAO Wenjiao, Dr. ZHENG Yongping etc.) from the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academ... Potassium-ion batteries (KIBs) are a compelling technology for large-scale energy storage due to their low-cost and large abundance. However, the development of potassium-ion batteries remains in i...
-
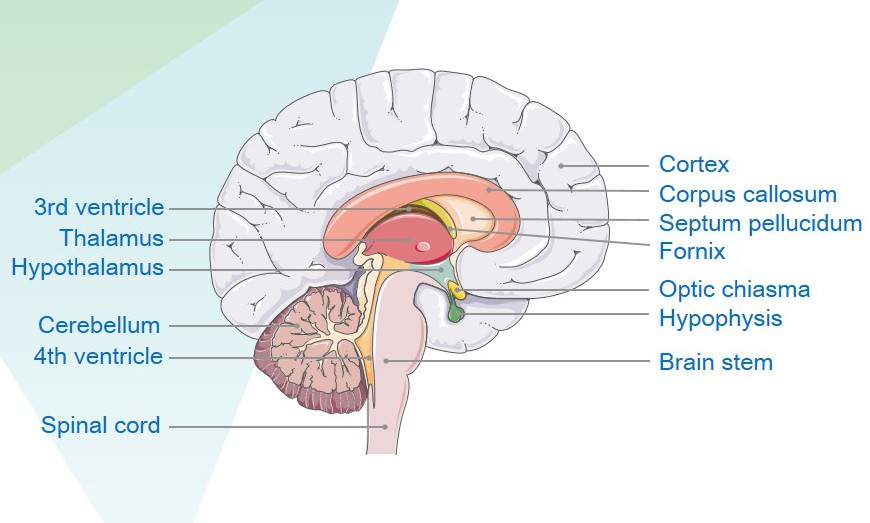
Mar 12, 2020Scientists Map Sexual Dimorphic Distribution of Cannabinoid 1 Receptor mRNA in BrainRecently, a research team focusing on the neural functions of the endocannabinoid system led by Dr. WANG Feng, from Brain Cognition and Brain Disease Institute of Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Tec... A major challenge in neuroscience lies in understanding how molecular and circuit differences in the brain synergistically contribute to sex differences in behavioral phenotypes. Sex differences in...
-
Mar 10, 2020Porcine Study Shows New Finger Size Ultrasound Capsule Endoscopy Capture Effective High-Resolution ImageShenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences introduced a novel μUSCE (micro-ultrasound capsule endoscopy), uses a capsule equipped with μUS (micro-ultrasound) transduc... A research team led by Prof. QIU Weibao from Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences introduced a novel μUSCE (micro-ultrasound capsule endoscopy), uses a capsule e...
-
Mar 06, 2020Researchers Introduce New Algorithm Substantially Reduce Machine Learning TimeResearchers from Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, introduced a simple DRL (deep reinforcement learning) algorithm with m-out-of-n bootstrap technique and agg... Researchers from Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, introduced a simple DRL (deep reinforcement learning) algorithm with m-out-of-n bootstrap technique and agg...
-
Mar 05, 2020Scientists Propose a Flexible Interface Design for Silicon-graphite Dual-ion BatteryA research group led by Prof. TANG Yongbing from the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, along with Prof. ZHENG Zijian from The Hong Kong Polytechn... Energy consumption has been amplified sharply in last decades, conventional energy sources are facing great challenges to meet the ever-increasing demand. Since the first commercialization in 1990s...
-
Feb 25, 2020Researchers Propose A High-Density sEMG Technique for Automatic Speech RecognitionA research team led by Prof. CHEN Shixiong from Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences proposed a high-density (HD) sEMG technique, using dense arrays of individual... The communication of words and speaking is a tremendously important way to engage in social interaction. The normal speaking process requires coordinated contractions of a mass of articulatory musc...
-
Feb 25, 2020Researchers Proposed Nano Coating Anti-fog SpraysScientists from Shenzhen Institute of advanced technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (SIAT) are reporting development of a new anti-fog protective goggles, successfully developed nano coatings wi... Nano coatings, as they’re commonly known, are liquids, when applied to the materials, fuse with the surface to form a glossy, long-lasting barrier that repels water.In response to the needs of med...