High-performance Composite Coatings on Microelectrodes for Neural Stimulation has developed
Date:30-08-2017 | 【Print】 【close】
Neural stimulation/recording microelectrodes have been widely used to investigate neural activities and regulate neural disorders, including hearing loss, blindness, Parkinson’s disease, etc. In recent years, smaller and more sophisticated microelectrode arrays that are capable of precise stimulation/recording for neuronal networks are of increasing research interest, which require the dramatic decrement of geometric area. For precise neural recording or stimulation purposes, high cathodic charge storage capacity (CSCc), low electrical impedance and the safe charge injection capability (CIC), as well as the biocompatibility, are considered critical to reduce power consumption and ensure safe, effective neural signal transport.
Professor WU Tianzhun, from Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology of CAS, has recently developed a high performance iridium oxide (IrOx)/platinum (Pt) nanocones, which is considered to be a novel composite coating, could fulfill the critical stability and low power consumption requirements for active implant such as the artificial retina. And the co-first authors, ZENG Qi, XIA Kai and SUN Bin, who microfabricated the flexible electrodes and developed the novel electroplating method.
The 3D Pt nanocones were introduced as an adhesion layer between Pt substrate and IrOx layer. This 3D mid-layer was nanorough and nanoporous which provided at least two benefits: 1. larger surface area due to its nanostructure to accommodate more IrOx mass in a less dense form; 2. providing an intermediate layer for IrOx deposition and promoting good adhesion to substrate. The achieved IrOx/Pt nanocones coated microelectrode has higher CSCc and CIC for pulse stimulation. A typical microelectrode modified with nanostructured IrOx/Pt nanocones coating had a low impedance down to 2.45 kW·cm2 at 1 kHz, and a CSCc up to 22.29 mC·cm-2, which was about 6, 2.8 and 2.7 times higher than that of those samples coated with bare Pt, Pt gray and IrOx, respectively. Furthermore, it demonstrated superior mechanical, electrochemical stability and CIC. This composite coatings with well-controlled nanostructure can be used in broader applications for high-performance stimulation or recording electrodes as well as neural prosthesis.
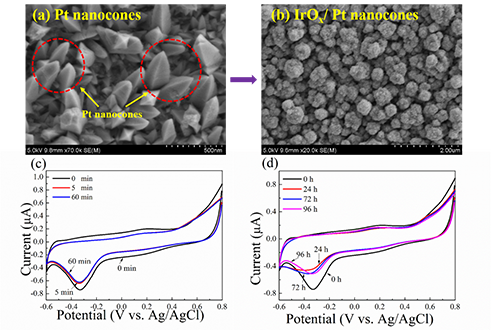
(a) Pt nanocones mid-layer, (b) IrOx/Pt nanocones composite coating, (c) Cyclic voltammograms of IrOx/Pt nanocones before and after ultrasonic treatment, (d) Cyclic voltammograms of IrOx/Pt nanocones before and after continuous stimulation.
The paper entitled with “Electrodeposited Iridium Oxide on Platinum Nanocones for Improving Neural Stimulation Microelectrodes” was published on Electrochimica Acta (http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.03.213) The preliminary results was also presented in IEEE international conference on Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular Systems (NEMS 2017), and was awarded “Finalist of best conference poster award”.
The full paper link: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.03.213
Contact:
Professor Dr. Tianzhun WU
Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: tz.wu@siat.ac.cn
