Scientists Develop Smartphone-Controlled Handheld Bioprinter for Skin Wounds Dressing
Date:22-11-2024 | 【Print】 【close】
A research team led by Prof. ZHAO Xiaoli from the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, together with collaborators, has reported a smartphone-controlled programmable handheld printer for in situ skin wounds dressing. This printer combines programmable control with handheld convenience, achieving a harmonious balance between high-precision printing and operational flexibility, making it particularly suitable for skin wound repair in challenging environments such as on battlefields or in remote areas.
The study was published in Advanced Science on Oct. 22.
Bioprinting technology has shown significant advantages in tissue and organ repair, yet its clinical application faces several challenges. The complex intermediate steps from fabrication to implantation hinder real-time patient treatment, while mismatches between scaffolds and wound shapes are frequent. Furthermore, the high costs and intricate procedures required for bioprinting restrict its broader clinical use.
In situ bioprinting technology, as a promising tool to overcome clinical translation barriers, prints bioinks directly onto wounds based on the specific characteristics of the injured area.
In this study, researchers proposed a novel in situ printing concept that combined programmable control with handheld operation, showcasing a self-developed programmable handheld bioprinter. The device employed both mechanical and pneumatic drive modes, enabling the extrusion of bioinks with different viscosities.
Controlled via a smartphone app, the bioprinter allows for flexible adjustment of printed strip sizes. Utilizing its programmable capabilities and high precision, it supports single or multiple bioinks and single or multiple layer structure printing. Equipped with a microchannel functional nozzle, it achieves gradient features and large-scale high-speed coating.
In both ex vivo and in vivo skin wound treatments, the proposed device demonstrated excellent performance in large-area coverage and wound closure.
This study provides an innovative tool for tissue regeneration, offering a new solution for efficient and immediate medical intervention.
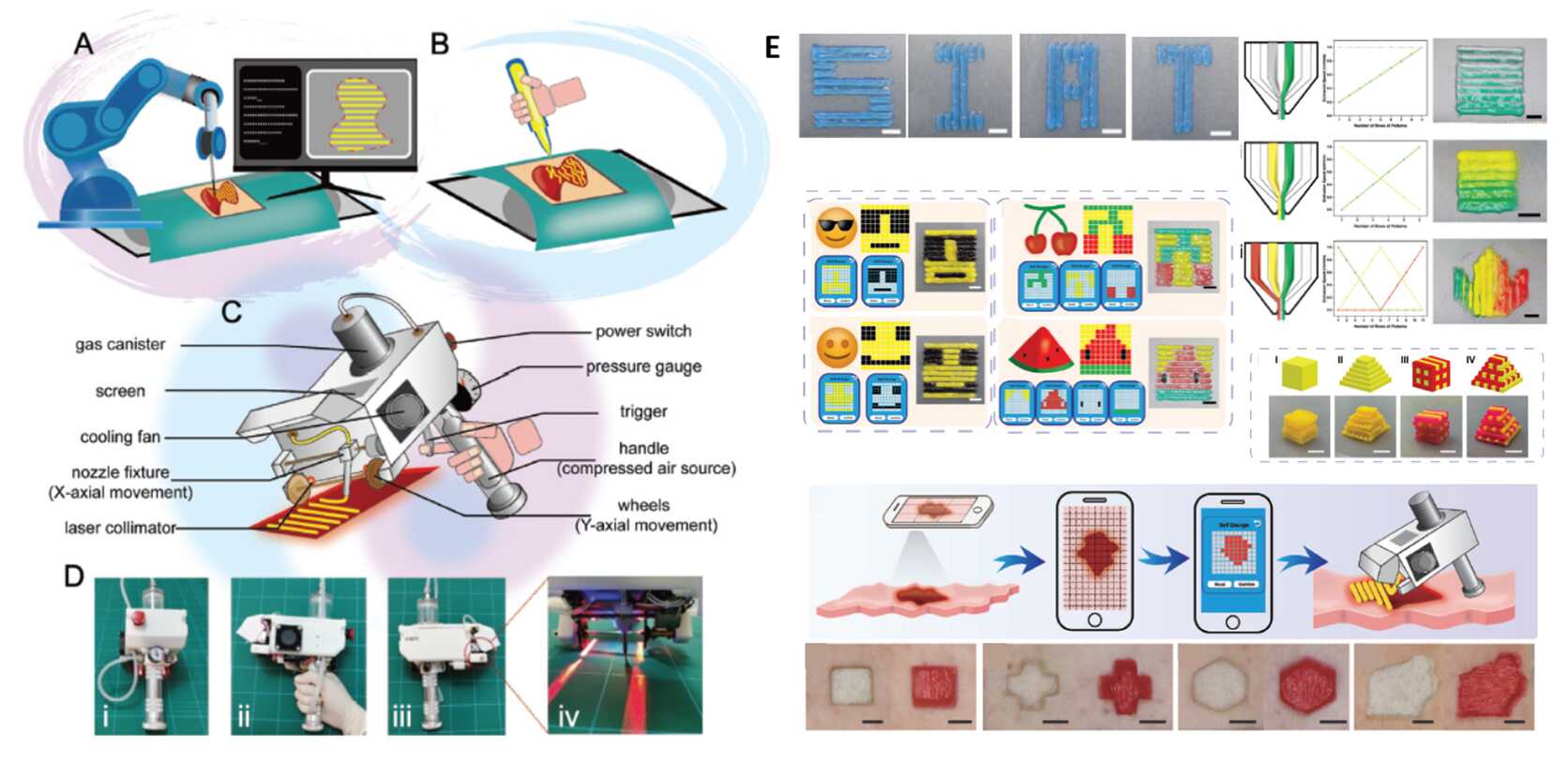
A handheld bioprinter controlled by a smartphone APP can accurately cover the skin wound with bioink, and perform in-situ repair on demand, providing efficient and accurate real-time treatment of large-scale skin wounds. (Image by SIAT)
Media Contact: LU Qun
Email: qun.lu@siat.ac.cn
Download the attachment: