Developing Bone-Targeting Exosome-Mimetics Gene Delivery System for Bone Regeneration
Date:10-10-2023 | 【Print】 【close】
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (MSC-exos) have shown great potential in the areas of bone regeneration and treatment of age-related diseases. However, low production yield and insufficient therapeutic efficiency of natural exosomes have limited their clinical applications.
Recently, a research group led by Prof. ZHAO Xiaoli at the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has constructed a bone targeting miR-26a loaded exosome-mimetics (EMs) delivery system for bone regeneration by activating Wnt signaling pathway.
This study was published in Chemical Engineering Journal on Jul.3.
The researchers fabricated EMs via sequential extrusion of MSC. EMs exhibited similar morphology, size distribution, and cellular uptake ability as natural exosomes. However, the production yield of EMs was 15 times higher than that of exosomes secreted from same number of cells.
The bone-targeting peptide Asp8 was modified on the surface of EMs (Asp8-EMs) via cooper-free click chemistry. Asp8-EMs showed good bone-targeting capacity in hydroxyapatite binding experiment in vitro and accumulated significantly higher on bone tissue of mice than those in control group.
Loading miR-26a in Asp8-EMs (Asp8-EM/miR-26a) via electroporation methods protected degradation of miR-26a in fetal bovine serum and enhanced osteogenic ability of Asp8-EMs, thereby realizing synergetic treatment for bone regeneration.
Bone regeneration ability of Asp8-EM/miR-26a was evaluated on bone defect mice model and osteoporosis mice model. Asp8-EM/miR-26a group significantly increased bone mineral density (BMD), bone volume fraction (BV/TV), and trabecular number (Tb.N) at 2 weeks and almost healed defect site at 4 weeks compared with other groups in bone defect mice. Asp8-EM/miR-26a group also prevented bone loss in osteoporosis mice compared with other groups at 4 weeks and 8 weeks. These results showed good bone regeneration behavior of Asp8-EM/miR-26a in both bone defect and osteoporosis models.
Underlying mechanism was investigated and revealed that miR-26a promoted bone regeneration by activating Wnt signaling pathway. Specifically, glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) could phosphorylate β-catenin and cause its degradation, miR-26a targets GSK-3β, inhibits GSK-3β expression and stabilizes β-catenin thereby leading to the accumulation of β-catenin for bone regeneration.
"Our study offers a strong and simple strategy for the generation of a considerable quantity of EMs within a brief time frame and customization of their functional attributes, thereby providing a promising cell-free therapy for specific disease," said Prof. ZHAO.
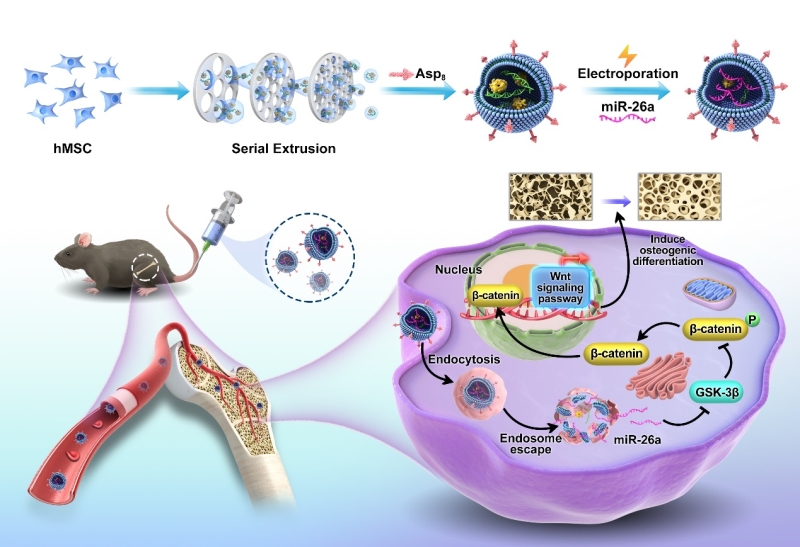
SchemeSchematic illustrations of constructing miR-26-loaded bone-targeting EMs for bone regeneration through targeting GSK-3β and then accumulating β-catenin to increase bone regeneration. (Image by SIAT)
Media Contact:
ZHANG Xiaomin
Email:xm.zhang@siat.ac.cn