Researchers Propose a Boundary-Aware Context Neural Network for the Medical Image Segmentation
Date:15-03-2022 | 【Print】 【close】
Automatic detection and recognition of lesions in medical images through artificial intelligence algorithms provides an economic, efficient, and effective computer-aided approach for clinical diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis monitoring. Furthermore, it makes a contribution to alleviating the labor intensity of radiologists, compensating the shortage of senior professional radiologists, and providing auxiliary imaging evidence.
Unfortunately, automatic lesion (organ or tissue) recognition in medical images remains several challenges: the sizes and shapes of lesion regions vary among individuals; in some cases, obvious individual differences increase the recognition difficulty; high-precision segmentation is prone to the low contrast between the lesions and background.
In order to solve these challenges of medical Image segmentation, the research team led by Prof. FAN Jianping and LI Ye from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of Chinese Academy of Sciences has proposed a boundary-aware context neural network.
Their research was published in Medical Image Analysis.
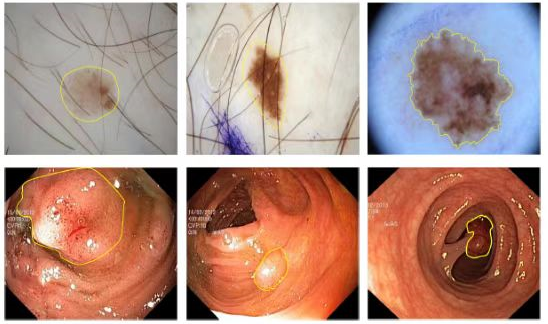
Fig.1. Examples of different modes of medical image (Image by SIAT)
In this study, benefiting from the designed pyramid edge extraction module, multi-task learning module, and cross-feature fusion module, multi-level and fine-grained image features are adaptively extracted, which improved the perception of the neural network on complex structures such as lesion shape, distribution, and edge information, and reduces the interference of surrounding normal tissues, organs, and noise. The proposed method has been quantitatively and qualitatively validated in various lesion segmentation tasks of multi-modal medical images, such as dermoscopy images, endoscope images, and X-ray images. Compared with other deep learning methods, this approach achieves state-of-the-art performance. Concretely, the recognition accuracy for the melanoma segmentation based on dermoscopy image is 81.0%; that for colon polyp recognition based on endoscope image is 88.5%; that for lung organ segmentation based on X-ray image is 92.8%.
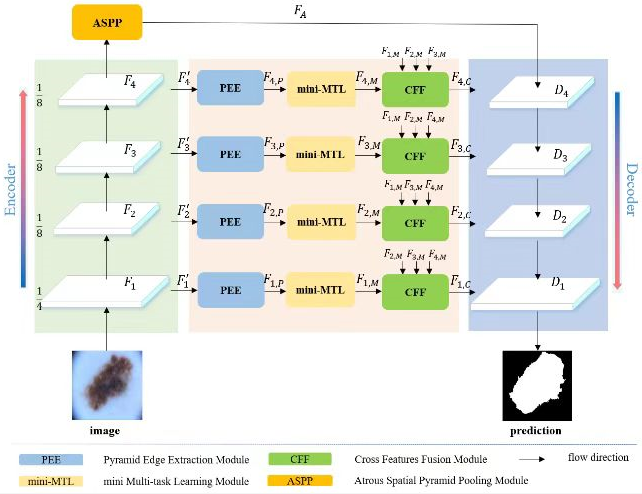
Fig. 2. Schematic diagram of context-aware deep neural network based on boundary information response (Image by SIAT)
"The target areas are accurately located with the aid of effective image context representations. This indicates that our model is able to simultaneously process fine structures and rectify errors, which can assist doctors to speed up the diagnosis process and better the diagnosis precision." said Dr. WANG Ruxin, the first author of this study.
Media Contact:
ZHANG Xiaomin
Email:xm.zhang@siat.ac.cn