Researchers Achieve Non-Invasive Blood Glucose Monitoring Based on ECG
Date:19-10-2021 | 【Print】 【close】
Patients with diabetes are suggested to monitor blood glucose (BG) regularly and maintain BG level within the physiological range through antidiabetic drugs. Therefore, monitoring BG ranges of patients at different time points is an essential part of diabetes care.
The conventional approach for BG range monitoring is finger-prick measurement, which is invasive, uncomfortable and expensive, more importantly, it is not befitting to provide continuous monitoring.
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a painless, noninvasive way to help diagnose many common heart problems in people of all ages, the ECG-based approach can be used for real-time monitoring of different BG ranges as well.
In a recent study published in the journal IEEE journal of biomedical and health informatics and selected as a featured article, Dr. NIE Zedong's group at the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences reported that BG range monitoring can be achieved noninvasively based on ECG.
In this study, an approach of fusing density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise and convolution neural networks (DBSCAN-CNN) was presented for ECG preprocessing of outliers and classification of BG ranges based ECG. Considering that the classification accuracy based on the single heartbeat of ECG waveform was relatively low, the evaluation strategy of majority-voting in a window of 10 pulses was employed.
Firstly, the heartbeats of ECG were preprocessed by using an unsupervised method based on density-based spatial clustering. Secondly, each heartbeat was used as the input for CNN model to achieve the preliminary classification of BG ranges. Furthermore, the strategy of majority-voting was adopted in the terminal of CNN to determine the final classification of the BG ranges. The important information of ECG, which guided the final classification decision, was visualized using the gradient-weighted class activation mapping (Grad-CAM) method. As an application of three different BG ranges monitoring based on ECG, prediabetes/diabetes screening can be achieved noninvasively and conveniently according to the classification result of BG ranges on the fasting state and 2-hour after oral glucose tolerance tests (OGTT).
The result showed that the percentages of accurate classification were 87.94% in low glucose level, and 86.39% in high glucose level. In addition, the sensitivity of prediabetes/diabetes screening based on ECG was up to 98.48%, and the specificity was 76.75%. Therefore, the proposed approach for BG range monitoring and prediabetes/diabetes screening may have potentials in practical applications.
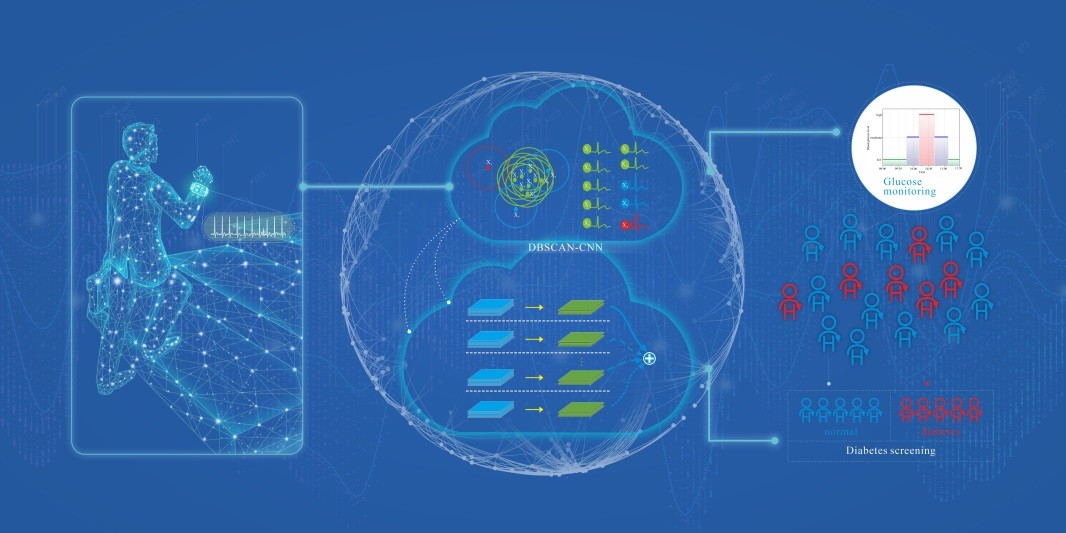
Diabetes screening and Glucose monitoring. (Image by Dr. NIE)
Media Contact:
ZHANG Xiaomin
Email:xm.zhang@siat.ac.cn