Researchers Reveal Novel Checkpoint Molecule of Natural Killer Cell Anti-Tumor Immunity
Date:15-10-2021 | 【Print】 【close】
Currently, rapid development of immunotherapy is revolutionizing the area of tumor therapy. However, most patients couldn’t benefit from available immunotherapy strategies due to limited efficacy and safety, especially under the setting of solid tumors.
Natural killer cells (NK cells) are cytotoxic innate immune cells, which play an important role in immune surveillance against tumors. However, the underlying mechanisms are still poorly understood.
In a study published in the journal Science Advances, Dr. TIAN Zhigang’s group at the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences reported that tumor necrosis factor–α (TNF-α)–induced protein-8 like-2 (TIPE2) suppressed NK cell maturation and anti-tumor immunity, indicated that TIPE2 is a checkpoint molecule of NK cells, and suggested that targeting TIPE2 might benefit NK –based tumor immunotherapy.
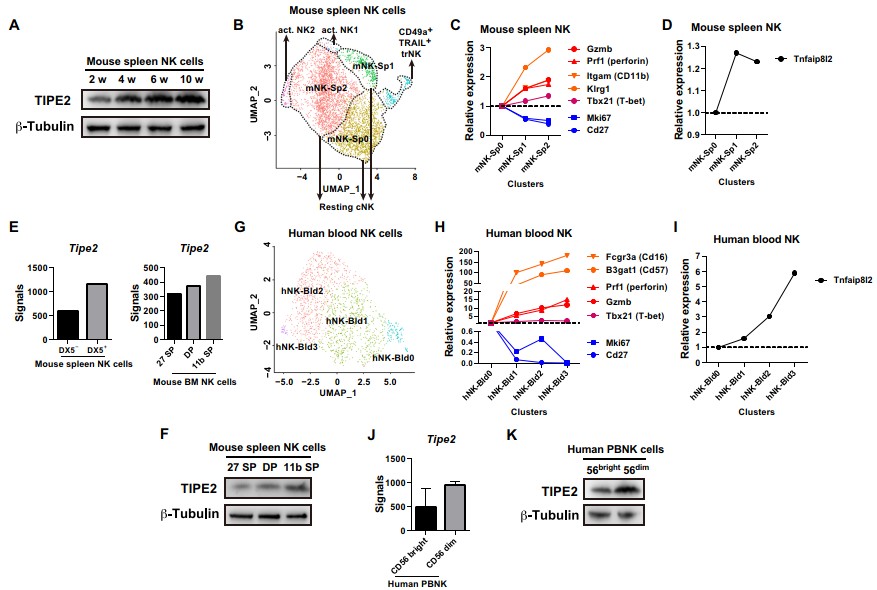
Figure 1. TIPE2 expression correlates with NK cell maturation. (Image by SIAT)
Previous studies of Dr. TIAN Zhigang’s group have already revealed the roles of checkpoint receptors T cell immunoglobulin and immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif domain (TIGIT) and A3AR on NK cell functions in tumor surveillance, tissue injury and regeneration. Based on these studies, they kept on searching for checkpoint molecules during NK cell maturation, the process during which NK cells acquire optimal functions. To this end, they performed single cell transcriptomic analysis of both human and mouse peripheral NK cells at the steady state. They found that either human or mouse NK cells are comprised of several sub-populations correlating with the NK cell maturation process from “immature” NK cells to “mature” NK cells. Importantly, TIPE2, a molecule previously reported to mediate immune tolerance, increases its expression along with the NK cell maturation process (Figure 1).
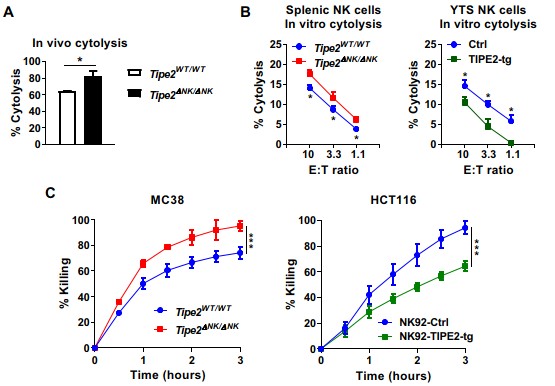
Figure 2.TIPE2 suppresses NK cell effector functions.(Image by SIAT)
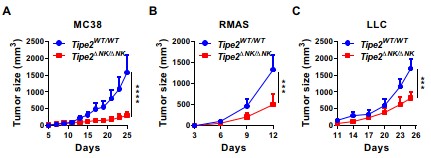
Figure 3.TIPE2 suppresses NK cell anti-tumor immunity in vivo. (Image by SIAT)
In order to investigate the role of this molecule in NK cell biology, the team generated the NK –specific TIPE2 deficient mice. In these mice, not only the levels of mature NK cells increased, but NK cells display enhanced effector functions (Figure 2), indicated that TIPE2 suppressed NK cell functional maturation.
Furthermore, NK –specific TIPE2 deficient mice showed better control of tumor growth in vivo (Figure 3), accompanied by increased tumor infiltration of NK cells, and by enhanced effector functions of tumor-infiltrating NK cells. Mechanistically, TIPE2 suppressed IL-15 –mediated activation of mTORC1 in NK cells.
Taken together, these data demonstrated that TIPE2 negatively regulated NK cell functional maturation and antitumor immunity.
Media Contact:
ZHANG Xiaomin
Email:xm.zhang@siat.ac.cn