Researchers Discover Late Development of Early Visual Perception
Date:14-10-2021 | 【Print】 【close】
Topological property (TP) is a basic geometric attribute of objects, which is preserved over continuous and one-to-one transformations. The number of holes in a figure is an example TP. For example, a bun (no holes) is topologically different from a doughnut (a hole). The human visual system has been shown to be highly sensitive to topological differences in images. Plenty of evidence shows that TP is processed prior to non-TP attributes of a visual stimulus, i.e., TP priority effect.
In a study published in the journal Child Development on September 27, Dr. HUANG Yan's group at the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences collaborated with Dr. CHEN Lin’s group at the Institute of Biophysics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences reported that the global topological priority in peripheral vision didn’t emerge until age ~10 years and the development of central and peripheral vision was different.
Evidence showed that children’s basic visual functions are similar to adults’, although have not fully matured. For example, the spatial contrast sensitivity among 4-year-old children follows a curve similar to that of adults, before reaching the adult level at 6 to 7 years.
This study investigated the global TP perception of 773 children aged 6 to 14, as compared to 179 adults. The results revealed that adults and children aged 10 or over showed a TP priority trend in both central and peripheral vision, i.e., less time was required to discriminate TP-differences than non-TP-differences. Children aged 6 to 8 showed a TP priority trend for central stimuli, but a reverse trend in their peripheral vision.
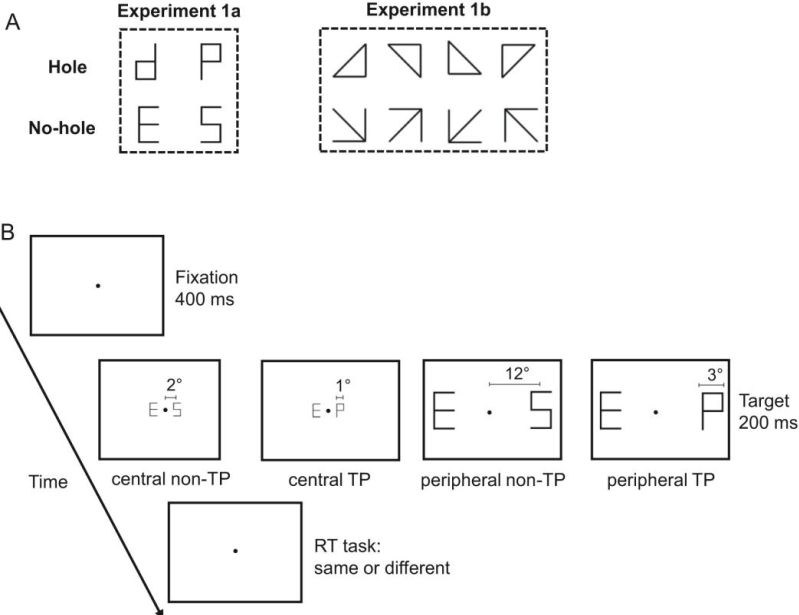
Example stimuli and experimental procedure.(Image by SIAT)
The TP discrimination tests provided a unique window into the development of the early stages of visual processing in children. This study discovered a significant difference in topological processing in peripheral vision between adults and children under the age of 10, which suggested that the global topological priority in peripheral vision does not emerge until age ~10 years.
Therefore, research on children’s TP perception and establishment of the corresponding norms for children of different ages may prove helpful for early and objective diagnosis of these diseases.
Media Contact:
ZHANG Xiaomin
Email:xm.zhang@siat.ac.cn