Researchers Demonstrate Black Phosphorus's Photochemical Activity for In Situ Biomineralization
Date:05-06-2020 | 【Print】 【close】
In recent years, two-dimensional black phosphorus (BP) with excellent near-infrared (NIR) photothermal and photodynamic effects, biocompatibility and biodegradability have captured extensive attention in biomedical applications, such as optical therapies, drug/gene delivery, bioimaging, and sensing.
Among them, the biodegradability of BP is the most important characteristic that distinguishes it from other inorganic two-dimensional photothermal materials, which can degrade into phosphate (PO43- ) in physiological environment.
Based on this, a research group led by Prof. YU Xuefeng from Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) cooperated with Prof. SHAO Jundong from Shenzhen University (SZU) has made new progress in the NIR light controlled in situ biomineralization of BP incorporated hydrogel.
In their work, the photochemical activity of BP sheets, which were reported by this group previously, arising from the formation of PO43- during NIR light-controlled biomineralization in situ was systematically investigated and demonstrated. Owing to the excellent NIR absorption, BP sheets under NIR illumination exhibited much faster degradation both in moist air and solution. The chemical activity of BP sheets was enhanced by NIR light irradiation.
The BP sheets not only could provide a phosphorus source and nucleation sites, but also accelerated the reaction between PO43- and Ca2+ to promote biomineralization.
The BP sheets with excellent photochemical activity were applied to controlled biomineralization of hydrogels in situ and by modulating the irradiation time and location of the NIR light, the mechanical properties and biomineralization ability could be tailored.
NIR light-controlled biomineralization has immense clinical potential especially tissue engineering and the photochemical activity of BP boded well for many other biological and biomedical applications.
This work entitled “Photochemical Activity of Black Phosphorus for Near-Infrared Light Controlled In Situ Biomineralization” was published in Advanced Science, and is supported by the National Natural Science Fund of China, Guangdong Special Support Program and Key Research Program of Frontier Sciences, CAS.
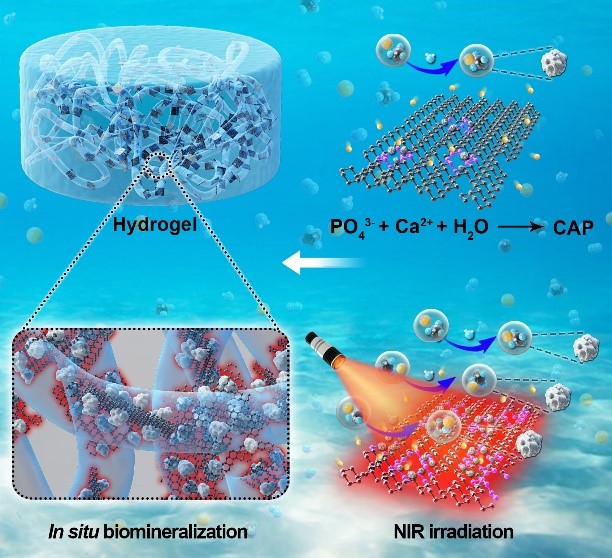
Fig. Schematic illustration of controlled biomineralization of BP-based hydrogel (Image by SIAT)
Media Contact:
ZHANG Xiaomin
Email: xm.zhang@siat.ac.cn