Scientists Propose Artificial Intelligence Based Parallel Imaging Method to Further Improve MR Imaging Speed
Date:02-04-2020 | 【Print】 【close】
Artificial intelligence (AI) makes it possible for machines to learn from experience, adjust to new inputs and perform human-like tasks.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), as a powerful imaging modality, can provide both functional and structural information of human bodies. But it has a bottleneck issue of slow imaging speed.
Dr. Shanshan Wang from the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, for the first time in the world introduced big datasets into accelerating MR imaging and reported it in the IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Prague, Czech Republic (2016).
Recently, she proposed a multi-channel image reconstruction method, named DeepcomplexMRI, to accelerate parallel MR imaging with residual complex convolutional neural network.
The study has been published in Magnetic Resonance Imaging.
Parallel imaging has been an essential technique to accelerate MR scan. Nevertheless, most traditional parallel imaging techniques only exploited prior information either directly from the to-be-reconstructed images or with very few reference images involved, they rely on the accurate estimation of the sensitivities and real convolutions even if big datasets are considered.
DeepcomplexMRI took advantage of the availability of a large number of existing multi-channel groudtruth images and used them as target data to train the complex deep residual convolutional neural network offline.
The methods enabled better images with less noise and artifacts than the conventional MRI, promoted fast MR imaging.
“There are many potentials of artificial intelligence based MR imaging. It will challenge the way of MR imaging from workflow, image acquisition, image registration to interpretation,” said Dr. WANG Shanshan, “we expect that MRI diagnostic radiographers may work alongside our ‘virtual colleagues’ in the future.”
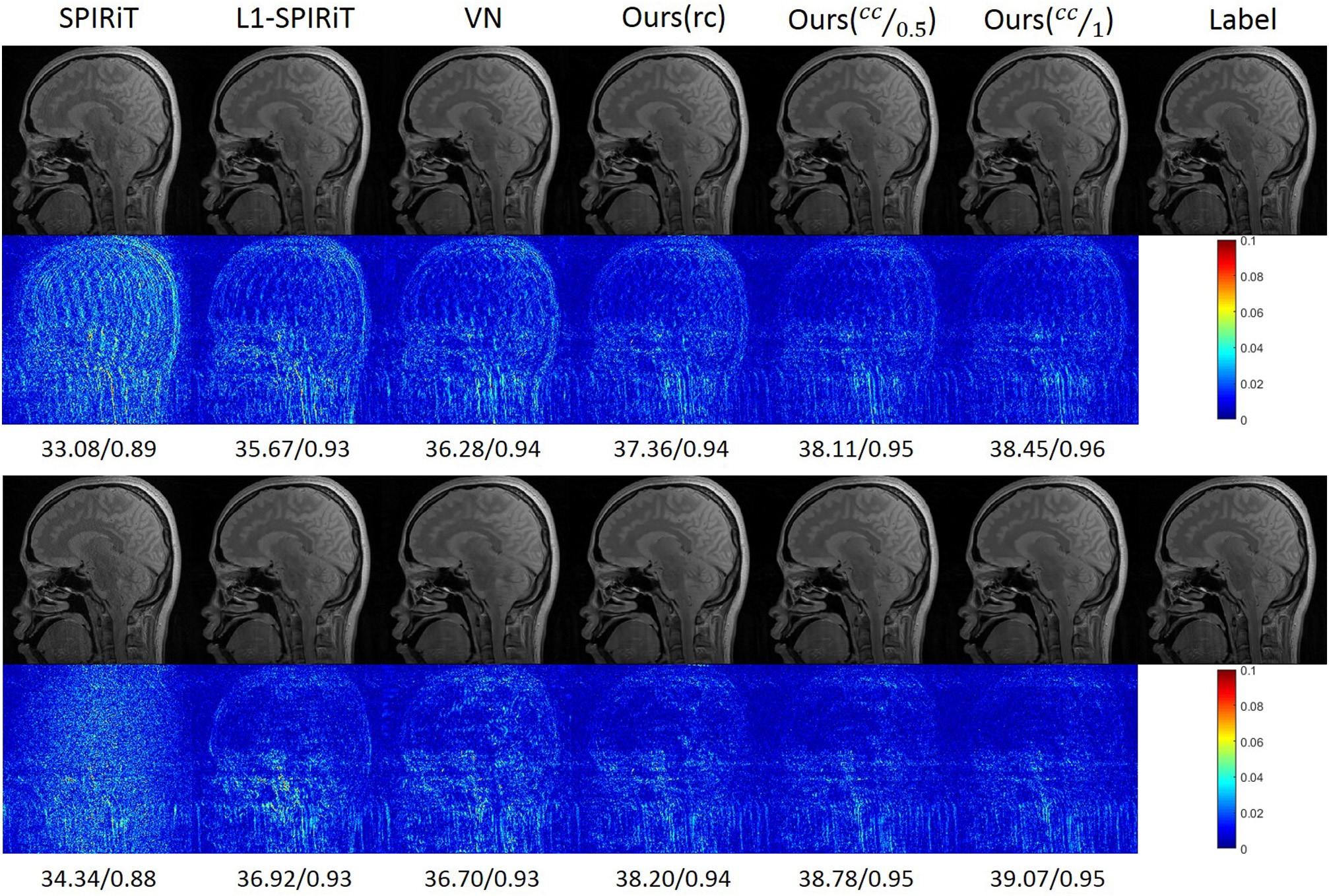
The comparison of SPIRiT, L1-SPIRiT, VN and the proposed method. (Image by Dr. WANG Shanshan)
Media Contact:
ZHANG Xiaomin
Email: xm.zhang@siat.ac.cn